Table of Contents
Introduction: What Is DevSecOps? And, What Does It Stand For?
The industry has been talking a lot about DevSecOps in recent years. DevSecOps, which stands for Development, Security, and Operations, encourages the need to integrate security best practices within every stage of the software development lifecycle.
Introduction To DevSecOps
Born from the school of thought which emphasizes the need for more secure software, DevSecOps (in short for Development Security Operations) is an approach to culture, automation, and platform design that promotes Security (Sec) as a shared responsibility between Development (Dev) and Operations (Ops).
Combining these three disparate teams into a single, cohesive process fosters collaboration and enforces security measures at every stage of the software development lifecycle, from early design and development to deployment and continuing operations.
Addressing The Need For Security In Software Development with DevSecOps
The need for DevOps Security arises from several factors, including the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, the growing reliance on software systems, and the potential impact of security breaches on individuals, organizations, and society as a whole.
Why is ‘Security' important in DevOps?
Here are some key drivers of security in software development:
- Protection against Cyber Threats
- Safeguarding Sensitive Data
- Compliance with Regulations
- Preservation of Business Reputation
- Minimizing Financial Losses
- Ensuring Software Reliability
- Mitigating Operational Risks
- Meeting Customer Expectations
Key Principles And Goals Of DevSecOps
To reiterate, DevSecOps was born out of the ideology of ‘Shift-left Security‘, meaning security practices should be implemented early and continuously within the DevOps workflow. The core principles of DevSecOps include security automation, continuous security, and cross-functional collaboration.
- Security automation – allows for consistent and repeatable security practices, such as automated testing, vulnerability scanning, and configuration management
- Continuous security – ensures that security controls are continually assessed and adjusted as needed
- Cross-functional collaboration – fosters communication and knowledge sharing among different teams, breaking down silos and enabling a holistic approach to security.
By addressing security early and continuously not only reduces the risk of vulnerabilities and breaches but also enhances the overall speed and efficiency of the software development process. By integrating security into DevOps practices, organizations can achieve a balance between speed, agility, and robust security measures, leading to more secure and reliable software applications.
Understanding DevOps vs DevSecOps
How does DevSecOps differ from traditional DevOps?
Read this blog to learn about DevOps vs DevSecOps in more detail.
Overview Of DevOps & Its Core Principles
The term ‘DevOps’ was coined by Patrick Debois in 2009, with the aim of fool-proofing the shortcomings of yesteryear software development process and practices, namely – SDLC, Waterfall model, Agile Development & Scrum among others.
DevOps addressed those issues with a unique approach approach to software development and delivery that emphasizes mainly on two things:
- Effective collaboration between different team members, and
- Improved automation in the overall software development cycle.
In order to improve the overall quality and reliability of software, DevOps promotes the need to constantly collect feedback by Continuously Monitoring the application for performance. But most importantly it introduced revolutionary practices such as Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Deployment and Continuous Delivery (CD).
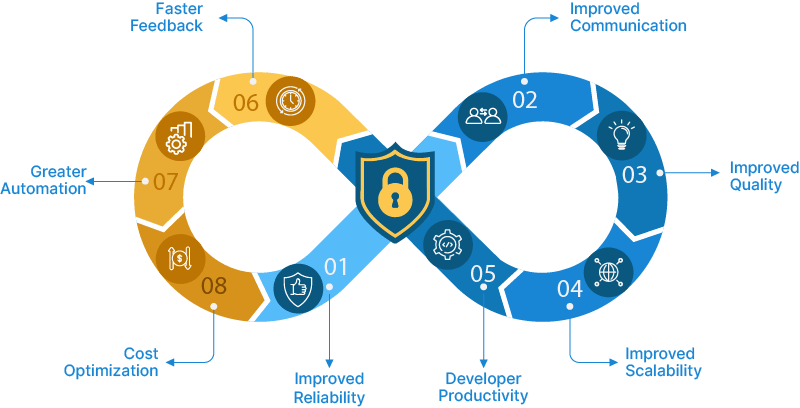
By improving communication, and automating manual processes, teams can break down organizational silos, thus helping them deliver better software, faster.
What Are the Benefits of Following the DevOps Methodology?
Organizations and teams benefit hugely from adopting the DevOps methodology. Some of them are:
- Frequent and reliable software updates due to the emphasis on Automation in general, CI and CD
- Improved communication and better collaboration leading to faster issue resolution, reduced bottlenecks, and improved overall efficiency
- Improved software quality thanks to continuous & automated testing, early bug detection and establishment of formal QA practices
- Improved developer productivity by automating manual tasks, such as build, test, and deployment processes
- Greater reliability and stability thanks to reduced human intervention and increased adoption of infrastructure as code (IaC)
- Continuous feedback and improvement by instilling a culture of continuous learning and improvement
- Scalability and flexibility in deploying and managing applications with ease based on demand
- Cost Optimization thanks to reduced manual effort, and improved resource utilization
What Is the Role of Security in DevOps?
In the context of Security, it is essential to understand that DevOps is the foundation upon which DevSecOps is built. DevOps promotes collaboration between development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams, breaking down silos and fostering a culture of shared responsibility. DevSecOps aims to integrate Security practices deeply and strongly into the DevOps workflow.
What Are the Challenges & Risks Associated With Neglecting Security in DevOps?
Neglecting security in DevOps can introduce various challenges/risks that can have severe consequences for organizations. Here are some of the key challenges and risks:
- Increased Vulnerability to Cyber Threats
- Higher Risk of Data Breaches
- Compliance and Legal Issues
- Operational Disruptions and Downtime
- Increased Remediation Costs
- Reputation and Customer Trust
- Lack of Accountability and Responsibility
- Missed Business Opportunities
To mitigate these challenges and risks, organizations should prioritize integrating application security throughout the entire DevOps process.
What led to the Rise in Shift-left Mentality?
By recognizing the importance of application security integration early and continuously throughout the software development lifecycle, DevSecOps builds upon DevOps principles by integrating security considerations, tools, and practices into the development and delivery process.
What does "Shift-left" mean in DevSecOps?
Add Your Heading Text Here
It emphasizes “shifting left”, meaning that security is addressed as early as possible in the development cycle, rather than being treated as an afterthought or a separate phase. This collaborative and integrated approach enables organizations to achieve a balance between speed, agility, and robust security measures, resulting in more secure and reliable software applications.
Key Processes & Tools in DevSecOps
Key Processes In DevSecOps
Here are the key processes typically involved in DevSecOps:
1. Code Analysis:
Code analysis involves examining the source code for security vulnerabilities, coding flaws, and adherence to coding standards. Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools analyze the codebase to identify potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities thereby helping developers fix security issues early in the development lifecycle.
2. Change Management:
Change management is the process of planning, coordinating, and controlling changes to the software system. Changes that impact security such as, code modifications, infrastructure updates, or configuration changes, should be properly reviewed, approved, and tracked. This helps maintain the security posture and stability of the system throughout its lifecycle.
3. Compliance Management:
Compliance management involves ensuring that the software and its development processes adhere to relevant regulations, industry standards, and security best practices. This involves assessing compliance requirements, implementing necessary controls, conducting audits, and documenting compliance activities. Compliance management helps organizations meet legal obligations and mitigate security risks.
4. Threat Modeling:
Threat modeling is a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating security risks by systematically identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and attack vectors to the software system. By analyzing the system’s architecture and design, threat modeling helps organizations prioritize security controls and countermeasures, ensuring that security risks are addressed effectively.
5. Security Training:
Security training is an essential component which involves educating developers, operations personnel, and other stakeholders about security best practices, secure coding techniques, emerging threats, and industry standards. Security training helps raise awareness, improve knowledge, and promote a security-focused mindset among the team members. It includes various techniques such as Static Application Security Testing (SAST), Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST), and Software Composition Analysis (SCA).
6. Incident Response and Recovery:
Incident response processes help organizations establish a response plan, assign roles and responsibilities, and conduct drills to practice incident response procedures. The process includes detection, analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery steps to handle security incidents effectively.
7. Vulnerability Management:
The vulnerability management process focuses on identifying, prioritizing, and remediating vulnerabilities. It includes scanning for vulnerabilities using automated tools, assessing their severity and impact, and establishing a process for timely remediation. This process often involves coordination between development and operations teams to address vulnerabilities promptly.
8. Secure Configuration Management:
Secure configuration management ensures that application and infrastructure components are configured securely. It involves establishing security baselines, following industry best practices for secure configuration, and regularly reviewing and updating configurations to address security vulnerabilities and compliance requirements.
9. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD):
DevSecOps integrates security practices into the CI/CD pipeline. Security tests, vulnerability scanning, and compliance checks are automated and integrated into the build and deployment processes. This ensures that security assessments are performed consistently and vulnerabilities are addressed before deployment.
10. Continuous Monitoring:
Continuous monitoring involves tracking and analyzing security events, application behavior, system performance, and user activities in real-time. It helps detect anomalies, security incidents, and potential vulnerabilities. Monitoring systems generate alerts for suspicious activities, providing valuable insights for incident response and security improvement.
Each of these processes contribute to the overall security posture of the software development and deployment lifecycle. They help identify and mitigate security risks, ensure compliance with regulations, and foster a culture of security awareness and accountability.
Tools Used In DevSecOps
To support the implementation of DevSecOps and the various processes explained in this article above, numerous tools can be used. Below is a list of tools that can be used across different stages of the software development lifecycle:
1. Static Application Security Testing (SAST) Tools:
– SonarQube
– Checkmarx
– Fortify
– Veracode
Static application security testing (SAST) tools analyze and find vulnerabilities in proprietary source code.
2. Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) Tools:
– OWASP ZAP
– Burp Suite
– Acunetix
– WebInspect
Dynamic application security testing (DAST) tools mimic hackers by testing the application’s security from outside the network.
3. Software Composition Analysis (SCA) Tools:
– Sonatype Nexus Lifecycle
– Black Duck by Synopsys
– WhiteSource
– Snyk
Software composition analysis (SCA) is the process of automating visibility into open-source software (OSS) use for the purpose of risk management, security, and license compliance.
4. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Security Tools:
– AWS Config
– Terraform
– CloudFormation
– Chef InSpec
5. Vulnerability Management Tools:
– Tenable.io
– Qualys
– Rapid7
– OpenVAS
Vulnerability management is the process of identifying, prioritizing, and remediating vulnerabilities by scanning for vulnerabilities using automated tools.
6. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools:
– Splunk
– ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana)
– IBM QRadar
– ArcSight
7. Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Tools:
– Jenkins
– Cloudbees
– Argo CD
– OpsMx Intelligent Software Delivery
8. Container Security Tools:
– Docker Security Scanning
– Twistlock
– Aqua Security
– Sysdig Secure
9. Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) Tools:
– Demisto (Palo Alto Networks)
– Phantom (Splunk)
– IBM Resilient
– Swimlane
10. Security Testing Frameworks:
– OWASP Testing Guide
– OWASP Application Security Verification Standard (ASVS)
– Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) tools and resources
These are just a few examples of common tools used in DevSecOps. The selection of tools depends on specific project requirements, technology stack, and organizational preferences. It’s important to evaluate and choose the tools that best fit your organization’s needs to enhance security throughout the software development lifecycle.
Benefits of Adopting DevSecOps
Here’s a dedicated blog covering the “Top 10 DevSecOps Best Practices” that teams can implement now.
What Are the Benefits of Adopting the DevSecOps Mindset?
- Early Risk Mitigation: Integrating security best practices from the start enables early vulnerability identification and mitigation, reducing the risk of security incidents
- Proactive Security Approach: Integrating security from the development phase ensures a proactive approach involving continuous monitoring, testing, and improvement, rather than a reactive approach
- Faster Issue Resolution: BAutomating security testing and continuous monitoring within the DevOps workflow enables swift identification and remediation of vulnerabilities and security issues
- Compliance and Regulatory Alignment: DevSecOps enforces early compliance with regulatory requirements, mitigating legal and financial risks associated with non-compliance
- Improved Collaboration: Involving developers, operations, and security teams early in development improves collaboration and cultivates a culture of security awareness
- Enhanced Software Quality and Stability: Early issue resolution, prevents vulnerabilities impacting software performance, reliability, and user experience, thereby enhancing overall quality and stability
- Strengthened Trust and Reputation: Embracing DevSecOps demonstrates a commitment to security and builds trust with stakeholders, ultimately enhancing an organization’s reputation and competitive edge
- Cost Savings: Early issue resolution through automated security testing prevents the costly need for emergency patches and post-deployment fixes, resulting in long-term cost savings.
Best Practices of DevSecOps
- Understand the current Security Posture:
First, assess the current security status of applications before implementing security measures or controls.
- Integration and Automation:
a. Emphasize automation over relying solely on point security or scanning tools.
b. Automation helps in scaling processes and reduces the risk of inconsistencies in manual activities or reviews.
- Integrating with the right tools for Deduplication and Collaboration:
Integration would help in deduplicating the results or the vulnerability root cause and help prioritizing the vulnerabilities to be fixed. This also helps in better collaboration.
- Avoid Rip and Replace:
a. When adopting new DevSecOps tools, focus on reusing existing features and investments for added value.
b. Avoid a complete rip-and-replace approach.
- Robust Monitoring and Log Analysis:
Implement a strong strategy for monitoring and log analysis to identify and respond to security incidents effectively.
- Shift Left Security:
a. “Shift left” by addressing security requirements and testing early in the software development cycle.
b. This includes conducting threat modeling, security code reviews, and security testing as integral parts of the development process.
About OpsMx
Founded with the vision of “delivering software without human intervention,” OpsMx enables customers to transform and automate their software delivery processes. OpsMx builds on open-source Spinnaker and Argo with services and software that helps DevOps teams SHIP BETTER SOFTWARE FASTER.

0 Comments